Software & Packages
Packages
We write high performing packages, mostly in Julia, related to acoustics and elastic waves, and more generally inverse problems from boundary measurements, such as stress and thermal predictions.
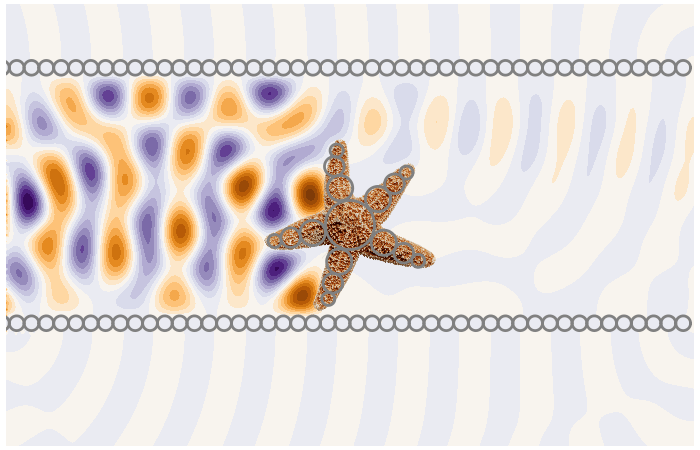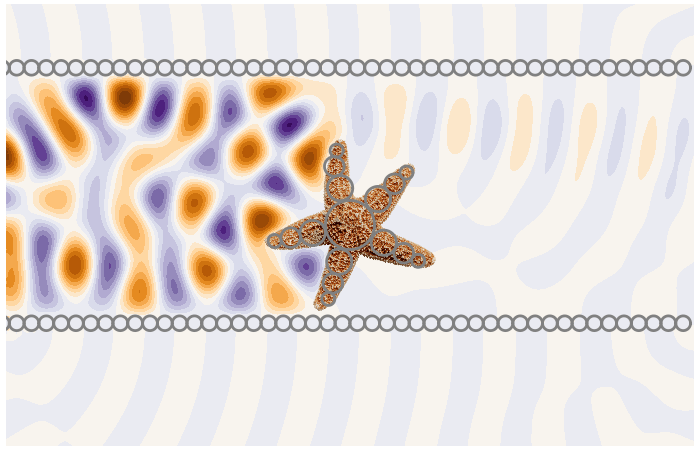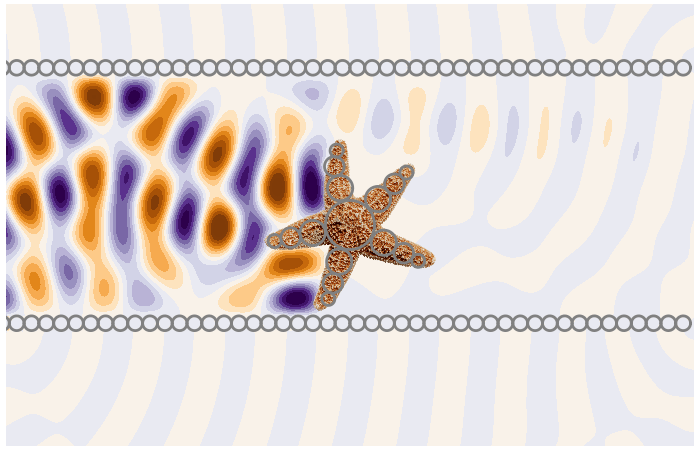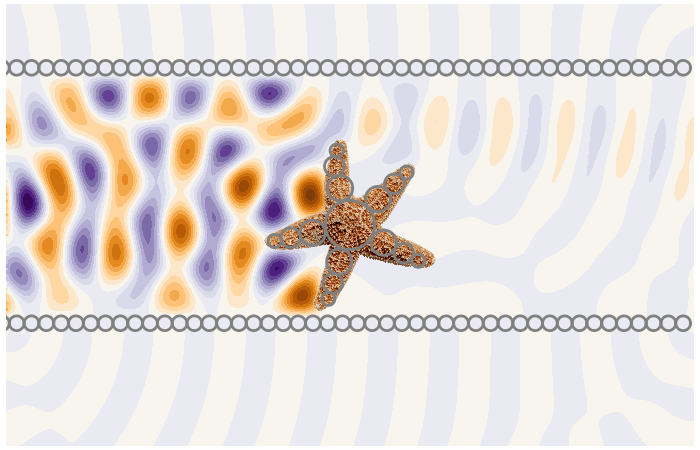
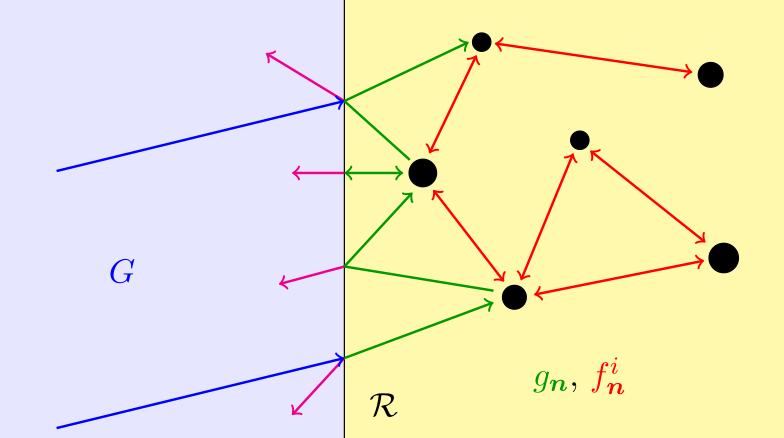
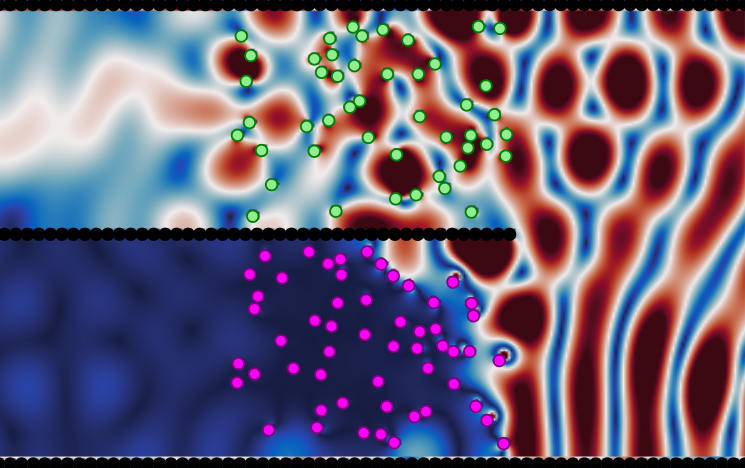
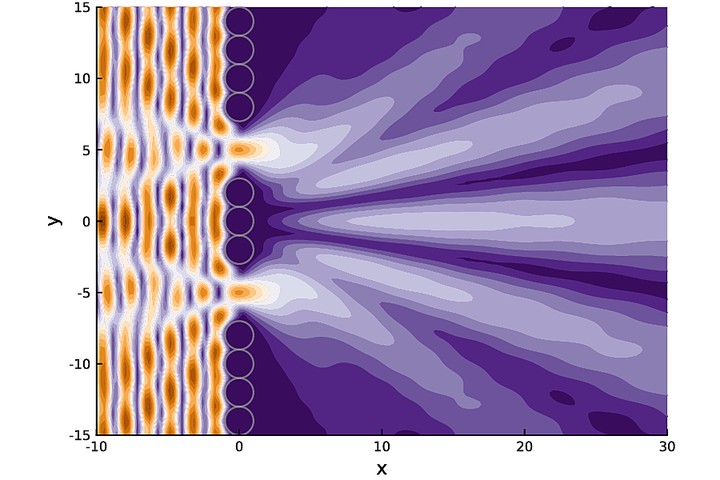
Under close inspection, many natural and synthetic materials are composed of small randomly distributed particles. To measure these particles we need to predict the multiple scattering of waves between the particles.
Calculates ensemble averaged waves in complex materials. A type of homogenisation method very useful for sensing.
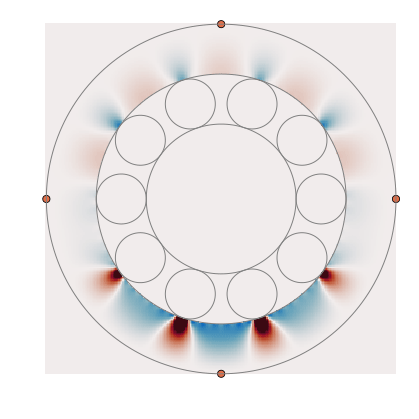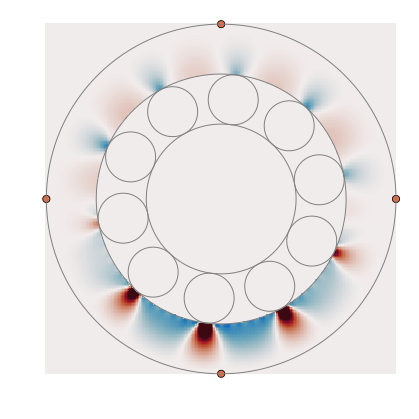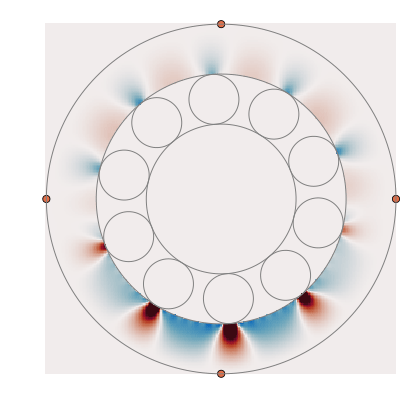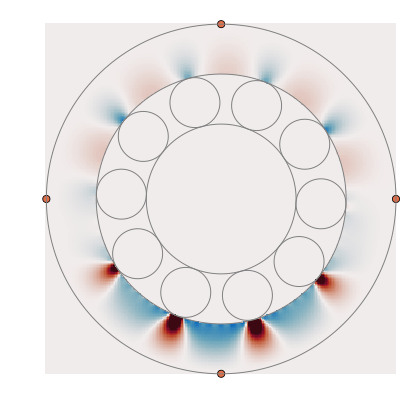
A package to calculate propagation and scattering of elastic waves in bearings. A great setting for inverse problems!
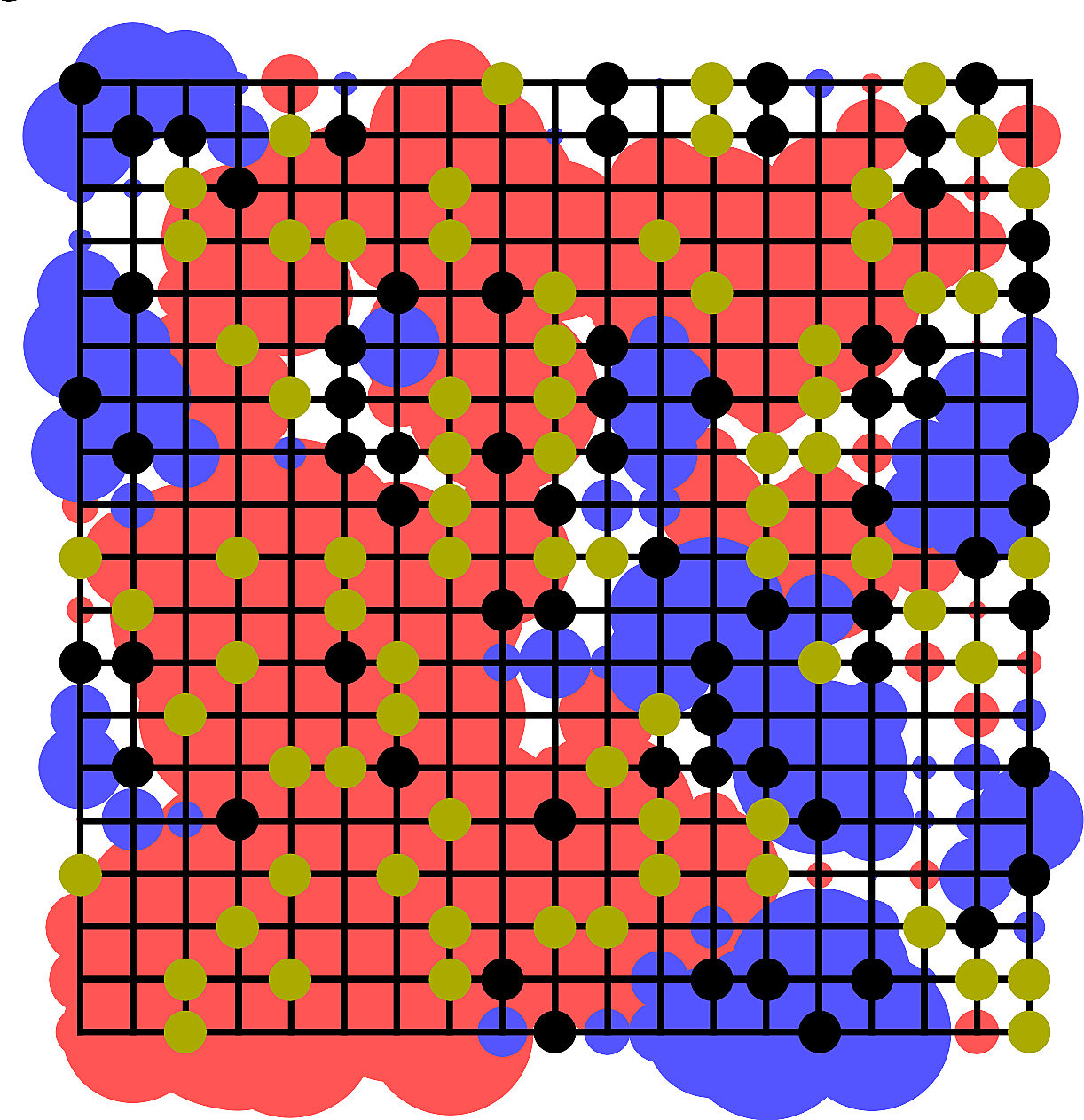
To calculate the current influence on a Go board we use entropy maximisation which is often used for intelligent decision-making.