Abstract
The Holzapfel–Gasser–Ogden (HGO) model for anisotropic hyperelastic behaviour of collagen fibre reinforced materials was initially developed to describe the elastic properties of arterial tissue, but is now used extensively for modelling a variety of soft biological tissues. Such materials can be regarded as incompressible, and when the incompressibility condition is adopted the strain energy Ψ of the HGO model is a function of one isotropic and two anisotropic deformation invariants. A compressible form (HGO-C model) is widely used in finite element simulations whereby the isotropic part of Ψ is decoupled into volumetric and isochoric parts and the anisotropic part of Ψ is expressed in terms of isochoric invariants. Here, by using three simple deformations (pure dilatation, pure shear and uniaxial stretch), we demonstrate that the compressible HGO-C formulation does not correctly model compressible anisotropic material behaviour, because the anisotropic component of the model is insensitive to volumetric deformation due to the use of isochoric anisotropic invariants. In order to correctly model compressible anisotropic behaviour we present a modified anisotropic (MA) model, whereby the full anisotropic invariants are used, so that a volumetric anisotropic contribution is represented. The MA model correctly predicts an anisotropic response to hydrostatic tensile loading, whereby a sphere deforms into an ellipsoid. It also computes the correct anisotropic stress state for pure shear and uniaxial deformations. To look at more practical applications, we developed a finite element user-defined material subroutine for the simulation of stent deployment in a slightly compressible artery. Significantly higher stress triaxiality and arterial compliance are computed when the full anisotropic invariants are used (MA model) instead of the isochoric form (HGO-C model).
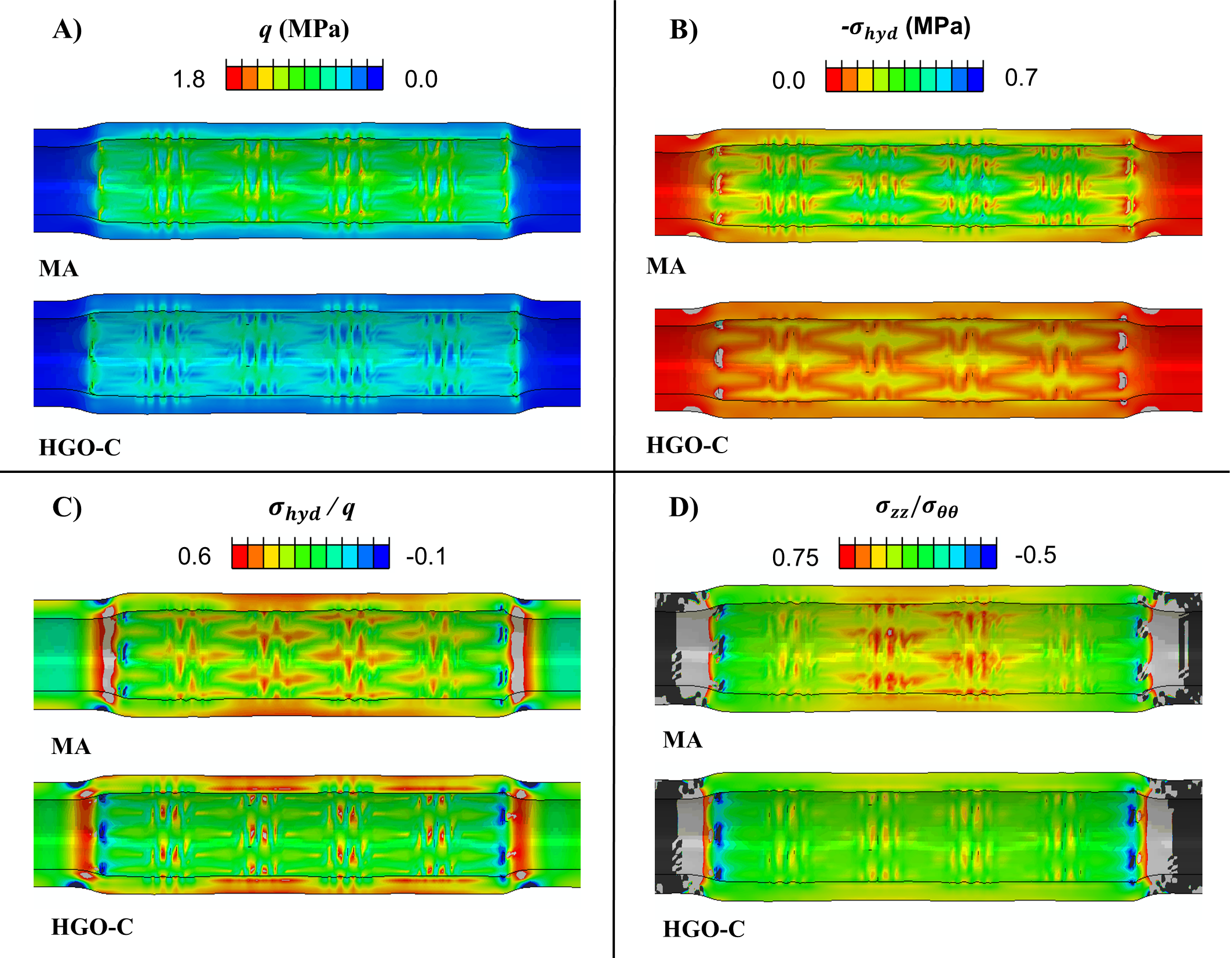
Modelling soft tissues has an immense potential to impact healthcare. It will enable a revolution of simulated surgeries, and long term predictions of prosthetics in the human body. Most soft tissues are reinforced by fibres (anisotropic). In this paper, we demonstrated how to implement, in finite element, robust models of anisotropic soft tissues. We were the first to correctly model volumetric changes in soft tissues, which, previously, were ignored by most finite element methods. To demonstrate the importance of our method, we simulated a stent deployed in an artery, and showed how the arterial forces were significantly under predicted with previous models.